As men age, many will experience issues with urination due to an enlarged prostate. But is this inevitable, or can you take steps to prevent it? Let's explore what causes prostate enlargement and the best ways to reduce your risk.
Understanding the Prostate and BPH
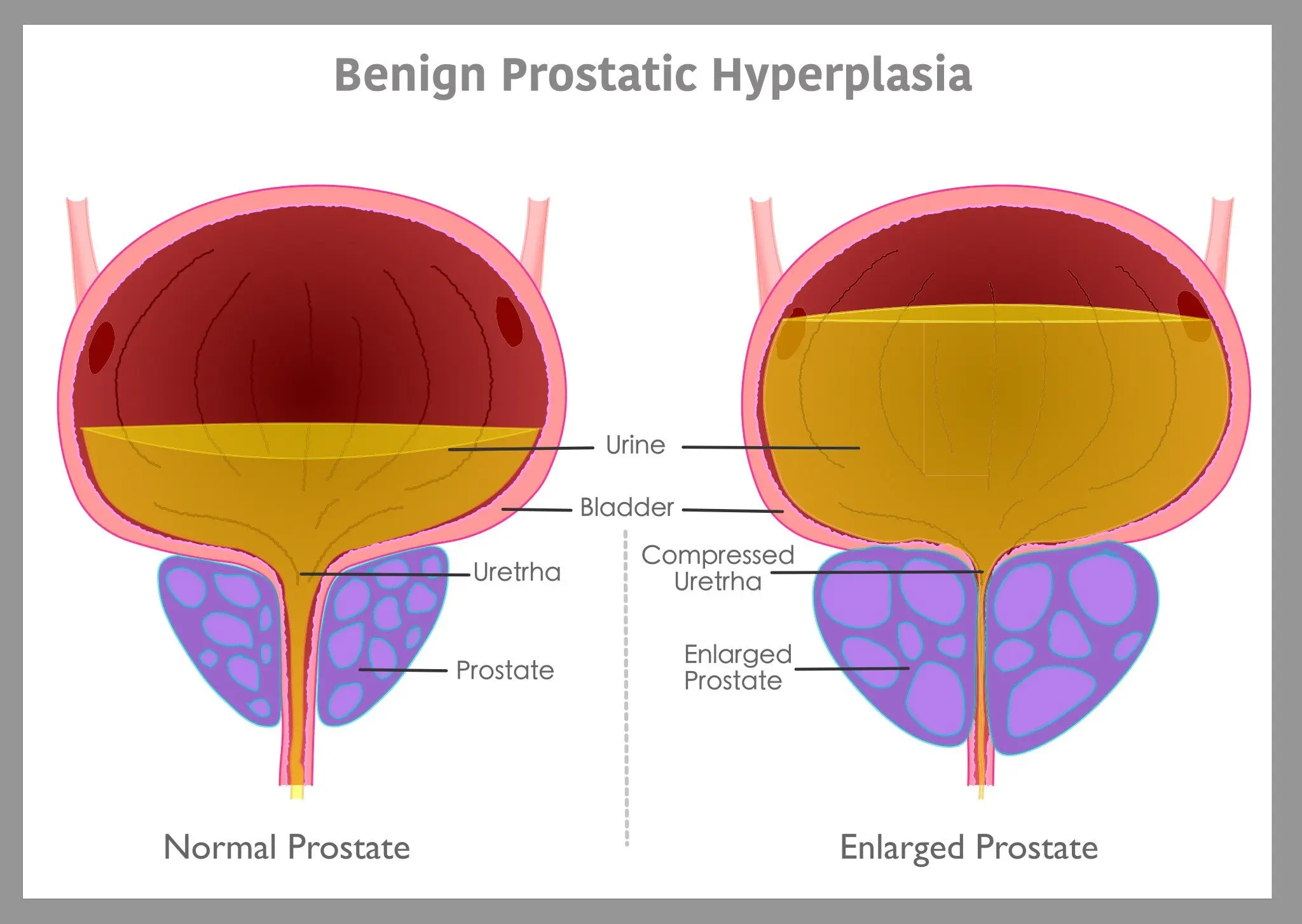
The prostate is a walnut-shaped organ that sits underneath the bladder, surrounding the urethra. While the prostate naturally grows during adolescence and early adulthood under the influence of hormones like testosterone, many men experience continued growth as they age—even while testosterone levels decline.
This condition, called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), occurs when there's an imbalance between cell growth and cell death in the prostate. The result is an increase in prostate cells, particularly epithelial and stromal cells.
What Causes BPH?
Several factors contribute to prostate enlargement:
- Genetics: BPH can be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. If your father had BPH, you're more likely to develop it too, especially if symptoms appear before age 60.
- Inflammation: This can be triggered by:
- Bacterial or viral infections
- Hormone changes
- Autoimmune conditions
- Urine refluxing into prostate ducts
- Changes in the prostate microbiome
- Inflammation releases cytokines from T-cells, which stimulate growth factors and cause cell proliferation. This creates a vicious cycle of growth, oxygen deprivation, more inflammation, and further growth.
- Increased smooth muscle tone: Regulated by the sympathetic nervous system, this can be affected by blood sugar changes, dietary factors, and obesity.
Four Ways to Prevent Prostate Enlargement
1. Avoid Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome—a cluster of conditions including diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure—significantly increases BPH risk. These conditions often result from the Western diet high in fat, red meat, simple carbohydrates, and sugar, combined with physical inactivity.
Research shows striking connections:
- Diabetes increases BPH risk by 125.5%
- Diabetes increases urinary symptoms risk by 95%
- BMI greater than 35 increases BPH risk by over 200% compared to BMI under 25
- Waist circumference of 42 inches increases risk by 138%
- Waist circumference of 40 inches increases risk by 48%
2. Increase Physical Activity
Exercise shows remarkable benefits for prostate health:
- Even light exercise decreases BPH risk by 30%
- Moderate to heavy exercise reduces risk by 36%
- Walking for more than 2 hours weekly (less than 20 minutes daily) reduces risk by 27%
- Burning 862 kilocalories per day reduced risk by about 50%
- Exercising six times per week showed a 51% reduction in risk
3. Avoid Certain Medications
While not strictly preventative, it's important to know that some medications can worsen BPH symptoms:
- Antihistamines: Can relax the bladder, making it harder to urinate
- Decongestants (like pseudoephedrine): Tighten smooth muscles, making urination more difficult
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Can negatively affect bladder function
4. Modify Your Diet
The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial, which followed over 18,000 men for seven years, provides our best data on diet and BPH:
- Reduce fat intake: Men with high-fat diets (38% of calories from fat) had a 31% higher risk of developing BPH compared to those with lower fat intake (less than 26%)
- Limit red meat: Daily red meat consumption increased BPH risk by 30% compared to eating it less than once per week
- Increase vegetables: Eating fewer than one serving of vegetables daily increased BPH risk by 38% compared to four servings daily
- Consider lycopene-rich foods: Lycopene, found primarily in tomatoes, may reduce BPH risk by 18%
About Lycopene
Tomatoes provide about 85% of our dietary lycopene intake. While studies show mixed results, the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial found an 18% reduction in BPH risk among those with lycopene in their diet.
For reference:
- 1 cup of tomato paste contains about 19mg
- 1 slice of watermelon provides 13mg
- 1 cup of cherry tomatoes delivers 3.8mg
Studies suggest that 6mg daily may be sufficient. Cooking tomatoes may increase effectiveness as the Maillard reaction creates additional antioxidant properties.
However, excessive tomato consumption can cause side effects including irritable bowel syndrome, bladder overactivity, acid reflux, and in rare cases, skin discoloration or kidney problems.
The Bottom Line
The strongest evidence for preventing BPH comes from:
- Regular exercise
- Following a Mediterranean-style diet rich in vegetables with moderate amounts of meat, fish, and healthy fats
- Avoiding conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol
These lifestyle modifications not only reduce your risk of prostate enlargement but promote overall health and wellbeing.

Comments · 1
connie headon
9 days agoThe best cure for enlarged prostate is 12mg to 15mg boron, nettle extract, lycopene, DMSO and vit D3 150 nmol/L (80ng/mL). PSA tests. Nighttime peeing is a typical enlarged prostate symptom. If you are japped or have acute covid, start on the 7mg nicotine patch until symptom free. The cure for prostate cancer is fenben, ivermectin and chlorine dioxide solution.
Today, 50% of American men over 50 have an enlarged prostate. By 80, that number jumps to 90%. 6 out of every 10 American men over the age of 65 have prostate cancer.
Optimise your vit D to 150nmol/L. Also take immune enhancing supplements,anti-inflammatory diet, good sleep, sun and walking.
High PSA is also a cause. As your prostate swells, your risk of prostate cancer increases. The risk that the cancer spreads to the bone of the spine, pelvis, skull, or femur. And that’s where 80% of prostate cancers move to. But boron has been proven to eliminate these problems.
One study found that boosting boron levels lowers your risk of prostate cancer by an incredible 64%. But boron does more than protect your prostate. It can also reverse the damage of an enlarged prostate.
Prostate tumors treated with boron were reduced by 38% and their PSA levels plummeted by 89%.
Boron seeks out and kills prostate cancer cells, leaving the healthy ones unharmed. It disrupts the protein building blocks needed to build the cancer cells and It speeds up cancer-cell death.
Foods that have the highest levels include avocados, prune juice, dried apricots.